|
AWS, data engineering, sql server, talend, postgres, business intelligence, car diy, photography
Search
Monday, 26 November 2018
Skoda Fabia (mk1) Fuse Layout
Wednesday, 21 November 2018
SQL SERVER IDENTITY vs POSTGRES SERIAL
What’s the POSTGRES equivalent of SQL SERVER’s IDENTITY column property?
SQL SERVER’s IDENTITY column property is often found when creating a table, and defining a column as int datatype (or biigint), with the IDENTITY property.
Create table dbo.some_table
(
my_primary_key int IDENTITY as primary key
, some_field varchar(10)
);The IDENTITY property helps auto-increment the field in SQL SERVER.
More details: MS link.
In POSTGRES, we follow a 2-step strategy.
1) Create (or alter) the table, and define the datatype as SERIAL.
Create table public.some_table
(
my_primary_key SERIAL primary key
, some_field varchar(10)
);
In the background, POSTGRES then creates a SEQUENCE that is used for this SERIAL column
public.some_table_my_primary_key_seq
2) Grant USAGE and SELECT to the users (or roles) that will insert into the table.
The owner of the table has all privileges on the table, and the sequence.
Other users do not.
Make sure the other users (or roles) have select and insert on the table
GRANT SELECT, INSERT on public.some_table to <other_users>;
To correct this, execute the psql:
GRANT USAGE, SELECT on public.some_table_my_primary_key_seq to <other_users>;
(replace <other_users> with the users/roles as needed)
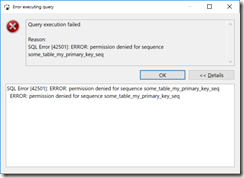
If step (2) isn’t followed, you are presented with an error message:
Query execution failed
Reason:
SQL Error [42501]: ERROR: permission denied for sequence some_table_my_primary_key_seq
(
in DBeaver, the error message looks like
)
Summary
In SQL SERVER, there’s the IDENTITY field property.
In POSTGRES, use SERIAL, and grant USAGE, and SELECT on the associated sequence.
Bonus tip
It may be easier to grant all privileges in a schema to the user.
grant all privileges on all sequences in schema public to some_user;
Script
--connect to postgres as user2 --reconnect to postgres as user1 set role user2; grant usage, select on public.some_table_my_primary_key_seq to user2; drop table public.some_table; --can only drop the table as the owner user1 |